在上篇文章中,我们分析了 Flutter 中主要由AnimationController控制动画的开始、结束,但是默认情况下其只能产生线性变化的 double 类型的 value,如果想随时间变化,让 Widget 产生 Size、Offset 等属性的变化,亦或者控制这些值变化的速度快慢,这时候就需要用到 Tween 和 Curve 了。
下图是 Tween/Curve/AnimationController 等类的关系简单示意:
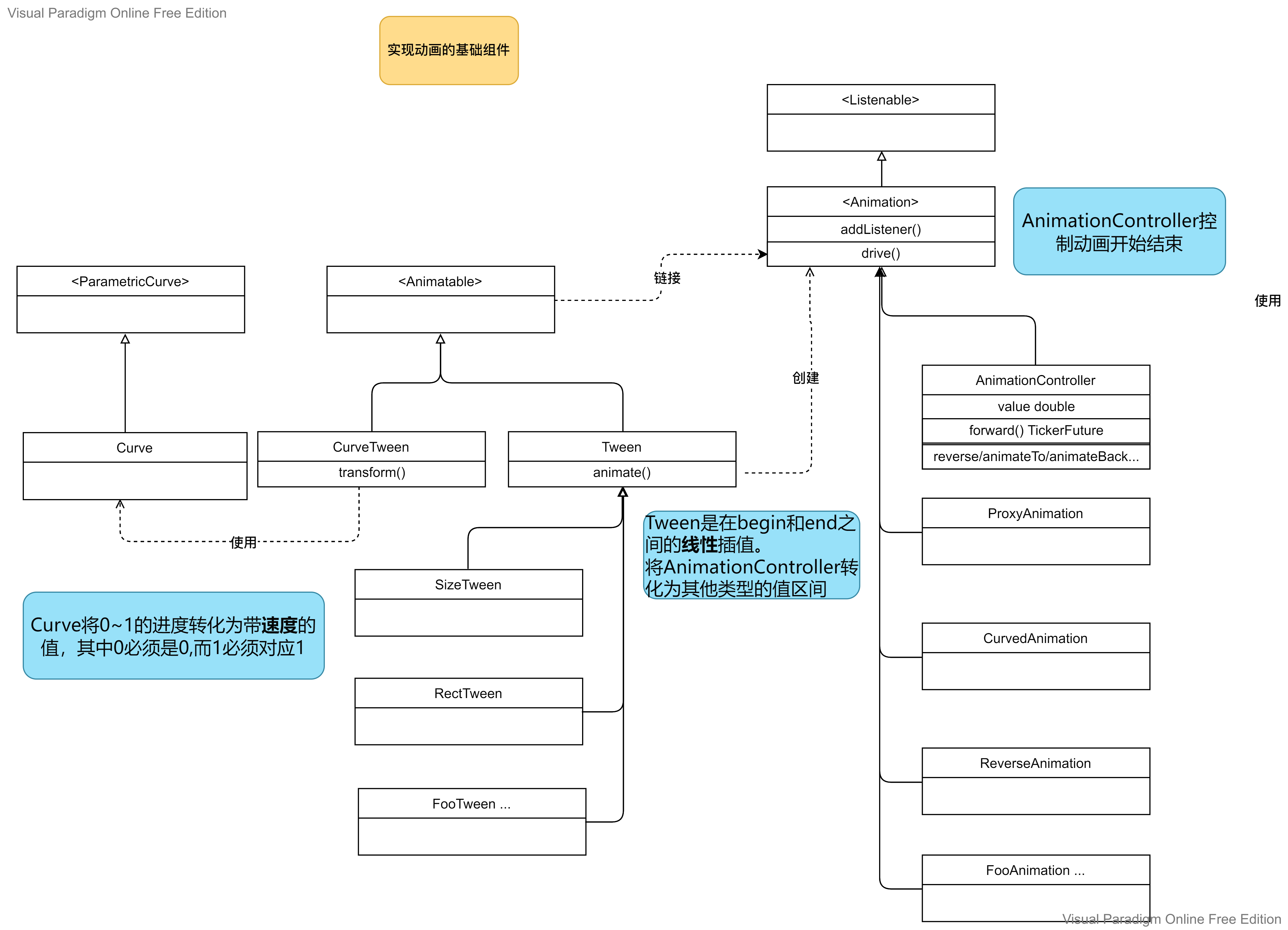
如上图所示:
- Tween 和 CurveTween 都继承自 Animatable,可以按照给定的 Animation<double>生产 T 类型的值,从而可以从 AnimationController 中衍生出其他类型的 Animation;
- 而 Curve 继承自 ParametricCurve,除了之前文章中分析的传入
AnimationController.animateTo和AnimationController.animateBack中从而作用于其创建的_InterpolationSimulation.x()方法之外,也可以被传入 CurveTween 或 CurvedAnimation 中,将 Curve 应用于 AnimationController。
上述关于 Tween 和 CurveTween 和 AnimationController 作用的方式,其实现都是依赖于 Animation<T> Animatable.animate(Animation<double> parent) 方法,根据传入的 Animation<double>(一般会是 AnimationController 对象)创建新的 Animation<T>(实际上是继承自 Animation 的_AnimatedEvaluation,其 Animation.value 取自 Animatable.evaluate(Animation<double>))。
源码分析
Animatable
An object that can produce a value of type
Tgiven anAnimation<double>as input.
Animatable 根据传入的Animation<double>对象创建 T 类型的对象,也就是说其将 Animation 产生的 double 类型“转化”为 T 类型,从而使得 Flutter 支持更加丰富的动画。
一般情况下这个
Animation<double>的值范围是[0.0,1.0],但是也可能超出此范围。
而这一切都通过他的animate方法实现:
Animation<T> animate(Animation<double> parent) {
return _AnimatedEvaluation<T>(parent, this);
}
在此方法中,将接收 Animation<double>对象作为parent,将自身作为_evaluatable属性创建了 Animation 的子类_AnimatedEvaluation 并返回:
class _AnimatedEvaluation<T> extends Animation<T> with AnimationWithParentMixin<double> {
_AnimatedEvaluation(this.parent, this._evaluatable);
@override
final Animation<double> parent;
final Animatable<T> _evaluatable;
// 主要逻辑,在这里调用 Animatable.evaluate,最终调用 transform(animation.value) 方法获取 Animation 对应的值
@override
T get value => _evaluatable.evaluate(parent);
...
}
再看一下 Animatable 的源码:
T evaluate(Animation<double> animation) => transform(animation.value);
T transform(double t);
其evaluate方法内部通过其唯一的抽象方法transform方法实现,Animatable 的各个子类也只需要实现transform方法即可。
除了上述与 Animation 有关的三个方法外,Animatable 还有一个链接两个 Animatable 的方法——Animatable.chain():
Animatable<T> chain(Animatable<double> parent) {
return _ChainedEvaluation<T>(parent, this);
}
与 Animatable.animate 方法类似,不同的是此方法返回的是 Animatable<T>的子类——_ChainedEvaluation
class _ChainedEvaluation<T> extends Animatable<T> {
_ChainedEvaluation(this._parent, this._evaluatable);
final Animatable<double> _parent;
final Animatable<T> _evaluatable;
// 关键方法,将 parent.transform 方法返回值传入 Animatable _evaluatable.transform 方法中并返回
@override
T transform(double t) {
return _evaluatable.transform(_parent.transform(t));
}
}
可以此方法作用是结合两个 Animatable 的效果。
Animatable 的主要作用是根据传入的 Animation 创建对应的 T 类型的值;其主要的子类有 Tween、CurveTween、TweenSequence。
TweenSequence 的作用于_chainedEvaluation 类似,只不过它可以将多个 Animatable 按照所占比重 weight 在 Animatable.transform 中应用。
Tween
A linear interpolation (插值) between a beginning and ending value.
Tween 是 Animatable 的主要子类之一,作用根据传入的 Animation(通常是 AnimationController)是在传入的begin 和 end 值之间创建线性的插值。
class Tween<T extends Object?> extends Animatable<T> {
// begin 和 end 可以为空,但是必须在实际使用到之前赋非 null 值
Tween({this.begin,this.end,});
// 这两个值可以随时修改
T? begin;
T? end;
@override
T transform(double t) {
if (t == 0.0)
return begin as T;
if (t == 1.0)
return end as T;
return lerp(t);
}
@protected
T lerp(double t) {
// 默认是按照当前的进度线性计算返回的值
return (begin as dynamic) + ((end as dynamic) - (begin as dynamic)) * t as T;
}
}
从 Tween 的源码可以看到,它实现了父类 Animatable.transform 方法,并在 t 在 (0.0,1.0) 之间时调用 Tween.lerp 方法获取对应的值,默认线性的在 T 上应用加减乘运算,并返回结果。Tween 的子类只需要重写 Tween.lerp 方法而非 Animatable.transform 方法。
这也就要求:
支持
lerp静态方法的类通常有对应的 Tween 子类,一般以 FooTween 命名,比如 ColorTween 就是借助 Color.lerp 方法实现:class ColorTween extends Tween<Color?> { // 如果需要渐变透明,请传入 null 而非 Color.transparent,后者实际是黑色透明,会导致渐变为黑色 ColorTween({ Color? begin, Color? end }) : super(begin: begin, end: end); @override Color? lerp(double t) => Color.lerp(begin, end, t); }Tween<T> 的类型 T 必须支持
+-*三种运算,并且返回值还是 T;对于 int 来说,因为 int*double=num 而非 int,有对应的特殊类:
- IntTween,使用 double.round 实现近似线性插值
- StepTween,使用 double.floor 确保结果永远不会大于使用 Tween<double>的值
在使用时,如果 Tween 确定不会变化,就可以将其保存在static final对象中以便在需要的地方共享同一个对象,而非在 State.build 方法中实时创建。
CurveTween
CurveTween 继承自 Animatable<double>,常见的用法是传入AnimationController.drive方法中获取一个新的 Animation<double>:
class CurveTween extends Animatable<double> {
/// Creates a curve tween.
///
/// The [curve] argument must not be null.
CurveTween({ required this.curve })
: assert(curve != null);
/// The curve to use when transforming the value of the animation.
Curve curve;
@override
double transform(double t) {
if (t == 0.0 || t == 1.0) {
assert(curve.transform(t).round() == t);
return t;
}
return curve.transform(t);
}
@override
String toString() => '${objectRuntimeType(this, 'CurveTween')}(curve: $curve)';
}
Tween 和 CurveTween 的主要区别在于,Tween 需要 T?类型的 begin 和 end 来创建线性插值,而 CurveTween 则需要 Curve 以便为 Animation<double>创建(非)线性插值。
Curve
ParametricCurve<T>是 Curve 的父类,其提供 ParametricCurve.transform 方法将 double t(在[0.0,1.0]之间)转化为曲线在 t 处对应的值 T t:
abstract class ParametricCurve<T> {
T transform(double t) {
assert(t != null);
assert(t >= 0.0 && t <= 1.0, 'parametric value $t is outside of [0, 1] range.');
return transformInternal(t);
}
@protected
T transformInternal(double t) {
throw UnimplementedError();
}
}
从其源码可以看出,ParametricCurve.transform 主要是检查入参是否合规,其主要逻辑在 ParametricCurve.transformInternal 中,一般子类只需要实现后者即可。
Curve 继承自 ParametricCurve<double>,也就是说它只能产生 double 类型的插值:
abstract class Curve extends ParametricCurve<double> {
/// Abstract const constructor to enable subclasses to provide
/// const constructors so that they can be used in const expressions.
const Curve();
@override
double transform(double t) {
if (t == 0.0 || t == 1.0) {
// 这里当 t 为 0.0 或者 1.0 的时候直接返回 t,避免了 double 运算后产生误差
return t;
}
return super.transform(t);
}
// 返回一个新的与之相反的 curve
Curve get flipped => FlippedCurve(this);
}
Curve 重写了父类的 transform 方法以规范对 double t 的处理,但还是建议子类只需要实现 ParametricCurve.transformInternal 方法。
我们以 Curve 的子类_Linear 为例,查看实现 Curve 的过程:
class _Linear extends Curve {
const _Linear._();
@override
double transformInternal(double t) => t;
}
总的来说,Curve 及其子类定义了一个曲线(可能是线性变化,也可能不是),并提供了double Curve.transform(double t)供使用者获取指定时间 double t 时曲线上对应的值 double。
Flutter 为我们预置了很多丰富的 Curve,可以在这里预览: Curves。
总结
经过上述分析,我们可以知道,无论是 Tween 还是 CurveTween,作为 Animatable,他们提供了Animation<T> Animatable.animatee(Animation<double> parent)方法,可以返回一个新的,相当于使用Animatable<T>.transform(double parent.value)计算Animation<T>.value的,Animation<T>。
而 Curve,只能通过double transform(double t)计算曲线在 t 位置的值的类,一般可以在 CurveTween、CurveAnimation 的构造方法或者 AnimationController 的 animateTo/animateBack 方法中,以便产生非线性的动画。
有想法?欢迎通过邮件讨论。